Are you building an electric circuit? Or let’s take it to a larger scale, an electric application. One of the most crucial steps of your project will entail gathering the required electronic components. These components when connected will form a complete electric circuit. Resistors are among the key components that you will need.
In This guide, we are going to discuss the essentials of resistors. You will learn what resistors are, their functions, and types, how they work, and what to look for when buying resistors.
What is an electronic resistor?
A resistor is a passive electronic component whose primary function is to limit the electric current passing through a circuit. It provides a significant level of “resistance” to the flow of electric current.
The resistance will eventually result in a lower voltage through that section or portion of the circuit. It is measured in ohms (Ω), which can be described as the resistance that is recorded when a current of one ampere (A), passes through a resistor with one volt (V) drop across the terminal. Usually the current is proportional to the voltage between the terminals. This relationship between the resistor, current, and voltage is represented by Ohm’s law: R=V/I
Resistors play different roles in electric circuits and applications. All the roles are based on the fact that they lower the current and voltage in electric circuits. Other reasons include regulating heat generation in circuits, gaining control, matching and loading circuits, and setting time constants among many other functions. Usually, the reason or purpose of including a resistor in a circuit will depend on the needs of an application.
Symbol of a resistor
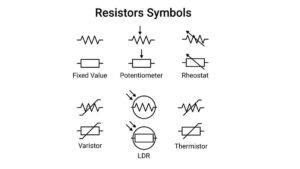
Resistors are usually represented by three different types of symbols. All the symbols show the connection between the resistor and the rest of the circuit.
The international IEC resistor symbol is rectangular with two leads at the end. The leads are the terminals and they represent the connection between the resistor and the rest of the electric circuit.
In the USA, the ANSI standard is used to represent the symbol of a resistor. It is a zigzag line with two connection lines at both ends of the resistor.
In some symbols, the resistance value is added next to the shape while in others it is not displayed. However, it is important to know the exact resistance value of a resistor when designing a circuit.
Types of resistors
Resistors come in different types. Various features and specifications define the type of resistor that is used in a circuit. Some resistors are through-hole while others are surface mount. Some are static while others are variable. Let’s take a look at the different types of resistors in the market and at the end of it all you will know which one is perfect for you.
- Fixed resistors: These are resistors that come with fixed resistance values. They tend to maintain this value throughout their lifetime.
- Variable resistors: These resistors allow the user to change or adjust their resistance values. The most common resistors under this category include potentiometer and rheostat.
- Still, under variable resistor type, there are special types of resistors whose resistance value depends on their physical quantity. They include:
- Thermistors: The resistance of these resistors depends on the temperature changes
- Photo resistors: In this type, the resistance is a function of the light level.
- Varistor: This is a type where the resistance is a function of the voltage level of a circuit.
- Magneto resistor: Under this type, the resistance is a function of the magnetic field
- Strain gauges: This is a type in which the resistance is a function of the mechanical load.
Another classification of resistors is based on the material that is used to make them. Some of the most common classifications include:
- Carbon composition
- Carbon film resistors
- Metal film resistors
- Metal oxide film
- Wirewound
- Foil
Each material has unique features and is designed for specific application areas. Various factors and properties have to be considered when choosing the resistor material. These factors include accuracy, cost, power, and many others. For example, metal and metal oxide resistor materials are known for their excellent thermal stability. On the other hand, wire wounds have a reputation for operating at high precision levels.
Resistor color code
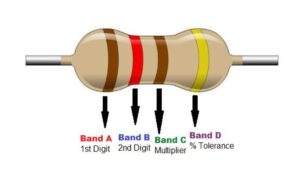
When buying resistors, it is important to pay attention to their color codes. This is vital because different color codes are used on resistors. The color codes represent the resistance values and also tolerance.
How do I read the resistor color code? Well, in most axial resistors the first two bands represent the actual resistance value. The third band is a multiplier while the fourth stands for tolerance. You can use any color code calculator online to verify this information.
Conclusion
I hope that with the information in this article, you are now in a perfect position to buy the best resistor for your application. Confirm the type, features, and specifications of the resistor before buying one. Finally, choose a reputable distributor such as Rantle, especially if you are planning to buy resistors in bulk.
